melbourne pathology test collection manual
Melbourne Pathology Test Collection Manual: An Overview
Welcome to the Melbourne Pathology Test Collection Manual! This comprehensive guide serves as an essential resource for healthcare professionals. It provides detailed information on proper specimen collection‚ handling‚ and storage. The manual ensures accurate and reliable pathology testing.
The Melbourne Pathology Test Collection Manual is a vital tool designed to support practitioners in obtaining timely‚ accurate‚ and high-quality diagnostic results. It serves as a comprehensive reference guide for healthcare professionals involved in the collection and handling of patient specimens. This manual aims to standardize procedures‚ ensuring consistency and reliability across all Melbourne Pathology collection centers;
Within this manual‚ you will find detailed instructions for various specimen types‚ including blood‚ urine‚ faeces‚ and swabs. Each section provides specific guidelines on collection techniques‚ required equipment‚ and appropriate storage conditions. Proper adherence to these instructions is crucial for maintaining specimen integrity and minimizing the risk of inaccurate test results.
Furthermore‚ the manual includes information on patient preparation‚ dietary restrictions‚ and safety protocols. By following these guidelines‚ healthcare providers can ensure the well-being of patients and minimize potential risks during the collection process. The Melbourne Pathology Test Collection Manual is regularly updated to reflect the latest advancements in pathology testing and best practices in specimen collection.
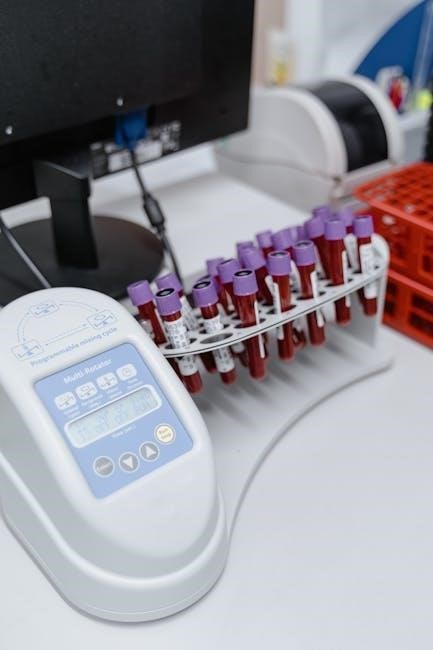
Specimen Collection Guidelines
This section outlines the essential guidelines for collecting various specimens for pathology testing. Adhering to these instructions ensures accurate results. It covers general instructions‚ blood‚ urine‚ swab‚ and faecal collection procedures for optimal outcomes.
General Specimen Collection Instructions
Proper specimen collection is crucial for accurate pathology results. Begin by verifying patient identity using at least two identifiers. Label all collection containers immediately with the patient’s name‚ date of birth‚ and collection date and time. Ensure the correct specimen type is collected for the requested test‚ referring to the test directory when necessary.
Use appropriate collection devices and follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully. Maintain strict aseptic technique to prevent contamination. Transport specimens to the laboratory promptly‚ adhering to specified temperature requirements. If delays are unavoidable‚ store specimens as indicated in the manual. Properly document any deviations from standard procedures.
Always prioritize patient safety and comfort during the collection process. Properly dispose of used collection materials to prevent cross contamination. Familiarize yourself with specific requirements for individual tests to ensure optimal specimen integrity. Consulting the pathology handbook is always a good idea.
Blood Collection Procedures
Blood collection requires meticulous attention to detail. First‚ verify the patient’s identity and confirm the requested tests. Gather all necessary supplies‚ including appropriate blood collection tubes‚ needles‚ and a tourniquet. Explain the procedure to the patient and obtain informed consent. Position the patient comfortably and apply the tourniquet above the venipuncture site.
Select a suitable vein‚ cleanse the area with antiseptic‚ and perform venipuncture using a smooth‚ controlled motion. Collect the required volume of blood into the appropriate tubes‚ following the correct order of draw to prevent contamination. Gently invert the tubes to mix the blood with additives. Release the tourniquet and apply pressure to the puncture site until bleeding stops.
Label the tubes immediately with the patient’s information and collection details. Dispose of used needles and supplies properly. Monitor the patient for any adverse reactions. Document the procedure and any relevant observations. Ensure prompt delivery of the specimens to the laboratory‚ maintaining appropriate temperature conditions.
Urine Collection Procedures
Proper urine collection is crucial for accurate test results. Several methods exist‚ each requiring specific instructions. For a routine voided sample‚ instruct the patient to cleanse the genital area before urination. The midstream clean-catch method is preferred‚ where the initial stream is discarded before collecting the sample.
For 24-hour urine collections‚ provide a large collection container and detailed instructions. The collection starts with emptying the bladder and discarding the first urine. All subsequent urine is collected over 24 hours‚ including the first void the following day. Refrigeration during collection is often necessary.
For catheterized urine samples‚ use sterile technique to collect the urine from the catheter port. For pediatric collections‚ use a urine collection bag applied to the perineum. Label all samples with the patient’s information‚ collection date‚ and time. Note any medications or dietary restrictions that may affect the results. Transport the samples to the laboratory promptly‚ following specified storage guidelines to maintain sample integrity.
Swab Collection Procedures
Swab collection is a common method for obtaining samples for microbiological testing. The procedure varies depending on the site being sampled. Generally‚ use a sterile swab and appropriate transport media. For throat swabs‚ vigorously swab the posterior pharynx and tonsillar areas‚ avoiding the tongue and cheeks. For nasal swabs‚ insert the swab into the nostril‚ gently rotate it against the nasal mucosa‚ and leave it in place for a few seconds.
For wound swabs‚ cleanse the area with sterile saline before swabbing the deepest part of the wound. Avoid swabbing superficial skin. For vaginal or urethral swabs‚ use a thin swab specifically designed for these sites. Insert the swab into the appropriate orifice and rotate gently to collect the sample.
After collection‚ immediately place the swab into the transport media. Label the swab with the patient’s information‚ collection site‚ date‚ and time. Ensure the swab is properly sealed to prevent leakage. Transport the sample to the laboratory as soon as possible‚ following specified storage guidelines. Different swabs and media may be required for specific tests‚ so consult the laboratory manual for details. Always use appropriate personal protective equipment during swab collection.
Faecal Collection Procedures
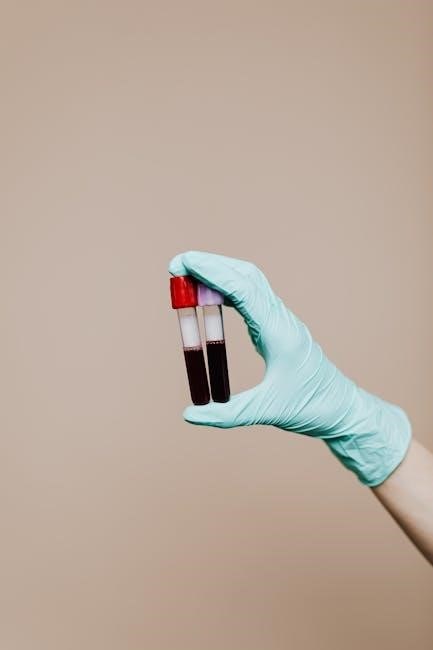
Faecal collection is essential for diagnosing various gastrointestinal conditions. The specific procedure depends on the test ordered. For routine faecal samples‚ instruct the patient to collect the specimen in a clean‚ dry container‚ avoiding contamination with urine or water. A small amount‚ about the size of a walnut‚ is usually sufficient.
For quantitative faecal collections‚ such as a 72-hour faecal fat test‚ provide the patient with a large collection container and detailed instructions. Emphasize the importance of collecting all stools passed during the specified period. The collection should begin and end with an empty bowel. The container must be refrigerated throughout the collection period.
For occult blood testing‚ follow specific dietary restrictions before and during collection to avoid false positives. Collect samples from three separate bowel movements. Certain tests‚ like those for parasites‚ may require specific preservatives. Immediately after collection‚ tightly seal the container and label it with the patient’s name‚ date‚ time of collection‚ and any relevant clinical information. Transport the specimen to the laboratory promptly‚ adhering to specified temperature requirements. Consult the laboratory manual for specific test requirements and any variations in procedure.
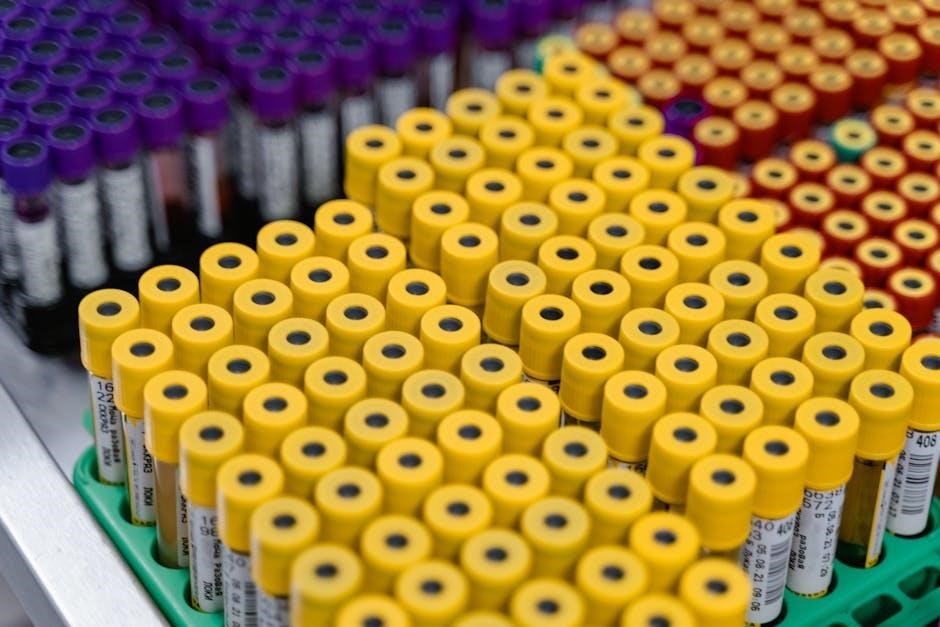

Specific Test Requirements
This section details specific instructions for individual pathology tests. These instructions cover proper collection‚ handling‚ and storage. Adhering to these guidelines ensures accurate and reliable results. Always consult this section before collecting samples.
Instructions for Blood Tube Samples
Proper collection and handling of blood tube samples are crucial for accurate pathology results. All tubes must be meticulously labeled with the patient’s full name‚ date of birth‚ and the exact date and time of collection. This ensures correct identification and traceability throughout the testing process.
It is imperative to adhere to the specific fill volume indicated on each tube to maintain the correct blood-to-additive ratio. Underfilling or overfilling can significantly impact test results‚ leading to inaccurate diagnoses.
The order of draw must be strictly followed to prevent cross-contamination of additives between tubes‚ which can compromise sample integrity. Gently invert the tubes immediately after collection to ensure thorough mixing of the blood with the anticoagulant or additive.
Avoid prolonged tourniquet application‚ as this can cause hemoconcentration and affect certain test values. Transport the samples to the laboratory promptly‚ maintaining the recommended temperature to preserve sample stability and prevent degradation.
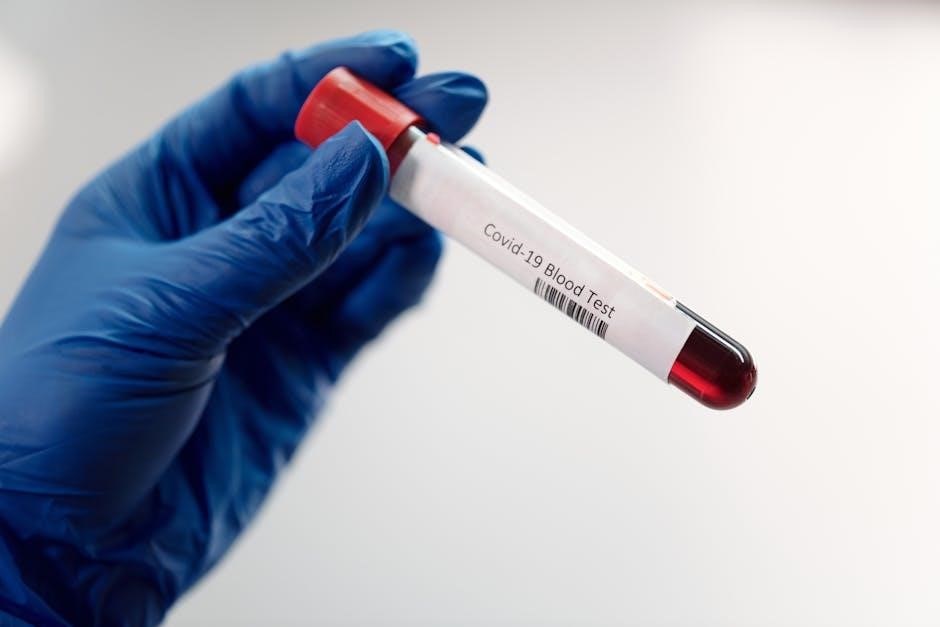
Always refer to the test-specific requirements in this manual for any additional instructions or precautions related to blood tube collection.
Requirements for 72-Hour Faecal Collection
The 72-hour faecal collection is a specialized procedure requiring meticulous attention to detail to ensure accurate results. Patients must be provided with clear and comprehensive instructions‚ including the appropriate collection container and any dietary restrictions.
The collection period should begin with the first bowel motion and conclude precisely 72 hours later. All faecal matter passed during this time must be collected and stored in the designated container‚ which should be kept refrigerated throughout the entire collection period to prevent bacterial overgrowth and sample degradation.
Patients should be advised to avoid contaminating the sample with urine or water‚ as this can affect the accuracy of the analysis. It is crucial to record the start and end dates and times of the collection accurately on the container label.
For certain tests‚ specific dietary restrictions may apply‚ such as avoiding red meat or certain medications. These instructions must be clearly communicated to the patient before the collection begins.
Once the collection is complete‚ the container should be promptly transported to the laboratory‚ maintaining refrigeration until delivery. Any deviations from these instructions may compromise the integrity of the sample and necessitate a repeat collection.
Spot Urine Sample Collection
Spot urine collection is a common procedure used for various diagnostic purposes; The accuracy of the results depends on proper collection and handling techniques. Patients should be provided with a sterile urine collection container and clear instructions on how to collect the sample.
Ideally‚ the first morning urine is preferred for certain tests due to its higher concentration. However‚ a random sample can be collected at any time of day if specified by the requesting doctor. Patients should cleanse the periurethral area with a provided antiseptic wipe before collection to minimize contamination.
The midstream clean-catch method is recommended: initiate urination‚ allow a small amount to pass into the toilet‚ and then collect the midstream portion into the sterile container. Avoid touching the inside of the container or lid to prevent contamination.
The sample should be properly labeled with the patient’s name‚ date‚ and time of collection. For specific tests‚ acidification of the urine sample within one hour of collection might be required to preserve certain analytes.
Dietary restrictions may also apply for spot urine HIAA. The collected sample should be transported to the laboratory as soon as possible. Prompt delivery ensures the integrity of the sample and the reliability of the test results.
Endocervical‚ Vaginal‚ and Urethral Swab Collection
Collecting endocervical‚ vaginal‚ and urethral swabs requires careful technique to ensure accurate and reliable results. Proper collection is crucial for diagnosing infections and other conditions. Use sterile swabs specifically designed for the target site‚ typically with a fine tip to minimize patient discomfort.
For endocervical swabs‚ insert the swab into the cervical os‚ rotate it gently‚ and hold for 10-30 seconds to collect sufficient cells. Avoid contamination with vaginal secretions. For vaginal swabs‚ gently insert the swab into the vaginal canal‚ rotate it against the vaginal walls‚ and withdraw.
Urethral swab collection in males requires inserting the swab 2-4 cm into the urethra‚ rotating it gently‚ and holding for a few seconds. In females‚ urethral swabbing is less common but involves similar insertion and rotation techniques.

After collection‚ immediately place the swab into the appropriate transport medium‚ typically a liquid-based medium with a pink lid. Ensure the swab is fully immersed in the medium to maintain sample viability. Label the specimen clearly with the patient’s information‚ date‚ and time of collection.
Transport the specimen to the laboratory as soon as possible‚ following specified storage guidelines. Proper handling and timely delivery are essential for accurate and reliable test results. Always consult the laboratory’s specific instructions for swab collection and transport.
Patient Preparation and Information
Proper patient preparation is vital for accurate pathology results. This section provides guidelines on pre-test instructions‚ dietary restrictions‚ and necessary information for patients. Following these instructions ensures reliable and meaningful test outcomes for diagnosis and treatment.
Patient Pre-Test Information
Ensuring patients are well-informed before undergoing pathology tests is crucial for accurate results. This section outlines essential pre-test information that should be communicated to patients. Clear and concise instructions minimize errors and ensure patient cooperation‚ ultimately improving the reliability of test outcomes.
Patients must understand the purpose of the test‚ the collection procedure‚ and any specific requirements they need to follow. This includes information about fasting‚ medication adjustments‚ and the timing of sample collection. Providing patient brochures and detailed instructions helps patients prepare adequately.
Furthermore‚ patients should be informed about potential risks or discomfort associated with the collection process. Addressing their concerns and answering their questions can alleviate anxiety and promote a positive experience. Effective communication enhances patient compliance and ensures the integrity of the specimen.
Ultimately‚ well-informed patients are active participants in the testing process‚ leading to more accurate and reliable pathology results that contribute to better healthcare decisions. Patient education is an investment in quality and patient well-being.
Dietary Restrictions for Specific Tests
Certain pathology tests require specific dietary restrictions to ensure accurate and reliable results. Failure to adhere to these restrictions can significantly impact test outcomes‚ leading to misdiagnosis or inappropriate treatment. This section details the dietary requirements for specific tests performed by Melbourne Pathology.
For instance‚ certain tests may necessitate fasting for a specified period‚ typically 8-12 hours‚ before sample collection. Other tests may require the avoidance of specific foods or beverages that can interfere with the analysis. It is crucial to provide patients with clear and comprehensive instructions regarding these restrictions.
The 72-hour faecal collection‚ for example‚ may have dietary guidelines to follow to have the most accurate results. Spot urine HIAA tests require dietary restrictions.
Healthcare providers must emphasize the importance of strict adherence to these dietary guidelines. Detailed written instructions‚ supplemented by verbal explanations‚ can help patients understand and comply with the necessary restrictions. Accurate dietary preparation is paramount for obtaining reliable and clinically meaningful pathology results.

Safety and Hygiene
Maintaining strict safety and hygiene protocols is paramount in pathology specimen collection. Proper hand hygiene and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) are essential to protect both healthcare workers and patients from potential infection risks.
Hand Hygiene and Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Adherence to stringent hand hygiene practices is a cornerstone of infection prevention within pathology collection settings. Perform hand hygiene meticulously before donning gloves‚ gowns‚ eye protection‚ and single-use surgical masks. Melbourne Pathology staff must use an N95 mask to ensure maximum respiratory protection.
Effective hand hygiene involves washing hands thoroughly with soap and water for at least 20 seconds or using an alcohol-based hand rub containing at least 60% alcohol. Proper hand hygiene is crucial before and after any patient contact‚ after removing PPE‚ and after touching potentially contaminated surfaces.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) serves as a vital barrier against infectious agents. This includes gloves to protect hands from direct contact with specimens‚ gowns to prevent contamination of clothing‚ eye protection to shield eyes from splashes‚ and masks to prevent inhalation of airborne particles. Proper donning and doffing procedures for PPE must be followed to avoid self-contamination.

Additional Resources
To further assist with proper procedures‚ refer to the tube guide for blood collection specifics. Consult the swab guide for appropriate swab selection and usage. These resources complement the manual’s instructions for optimal results.
Tube Guide
The Tube Guide is an indispensable tool within the Melbourne Pathology Test Collection Manual‚ offering a comprehensive overview of blood collection tubes. It details the various types of tubes used for different pathology tests. Correct tube selection is paramount for accurate results. The guide specifies tube color‚ additive‚ and fill volume requirements for each test.
Each tube type contains specific anticoagulants or clot activators‚ which are crucial for the integrity of the sample. The guide provides visual aids‚ illustrating each tube with its corresponding color code. This visual clarity aids in quick identification and reduces the risk of errors during collection.
Furthermore‚ the Tube Guide outlines the order of draw‚ a critical sequence to prevent cross-contamination between additives. Following the correct order ensures that additives from one tube do not affect the results of subsequent tests. The guide also includes information on proper mixing techniques after collection to ensure adequate interaction between the blood and the additive. This section ensures a standardized and reliable blood collection process. It minimizes pre-analytical variables that can impact test outcomes.
Swab Guide
The Swab Guide‚ a vital component of the Melbourne Pathology Test Collection Manual‚ offers detailed instructions for collecting swab specimens. This guide covers various swab types and their appropriate uses for different microbiological tests. Selecting the correct swab and following proper collection techniques are crucial for accurate diagnostic results.
The guide categorizes swabs based on their material (e.g.‚ cotton‚ rayon‚ flocked) and the transport media they require. It provides specific instructions for collecting samples from various anatomical sites‚ including the throat‚ nasal passages‚ wounds‚ and genital areas. Detailed illustrations and diagrams demonstrate the correct swabbing technique for each site‚ ensuring adequate sample collection.
Furthermore‚ the Swab Guide emphasizes the importance of avoiding contamination during the collection process. It outlines steps to minimize the risk of introducing external microorganisms that could compromise test results. The guide also provides information on proper storage and transportation of swabs to maintain sample integrity until they reach the laboratory. This section ensures that specimens are handled correctly‚ preventing false negatives or positives due to improper collection or storage. The Swab Guide is an essential resource for healthcare professionals seeking reliable and accurate microbiological testing.
